-
Posted on: 01 Aug 2024
-
Your FICO score is a crucial three-digit number that significantly impacts your financial life. It dictates whether you'll be approved for loans, credit cards, and even rental agreements. A FICO score of 700 is often considered a good starting point, but how common is it? Understanding the distribution of FICO scores and where you stand is essential for financial planning and achieving your goals.
Understanding the FICO Score Range
Before delving into how many people have a 700 FICO score, let's understand the FICO score range. FICO scores range from 300 to 850, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. The FICO scoring model is used by the vast majority of lenders to assess risk.
Here's a general breakdown of the FICO score ranges and their associated creditworthiness:
- 300-579: Poor credit
- 580-669: Fair credit
- 670-739: Good credit
- 740-799: Very good credit
- 800-850: Exceptional credit
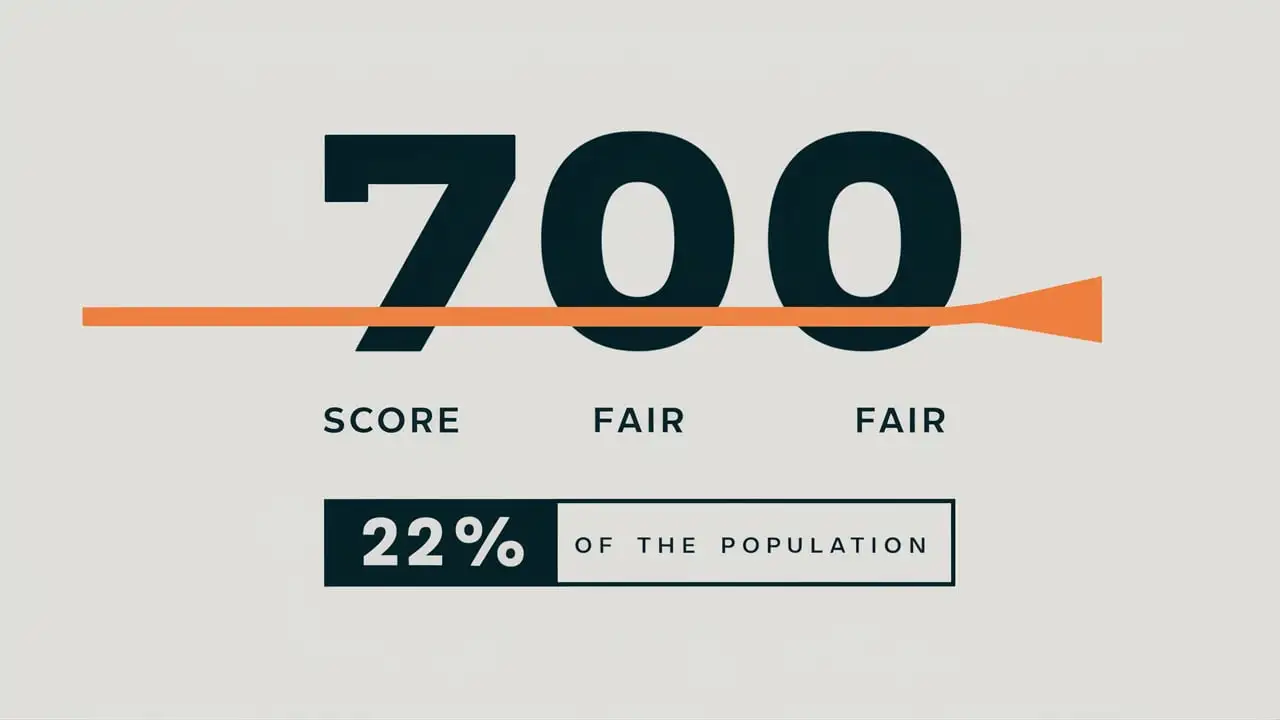
As you can see, a FICO score of 700 falls within the "Good" credit range. This means you're generally seen as a reliable borrower, but there's still room for improvement to achieve "Very Good" or "Exceptional" credit.
The Prevalence of a 700 FICO Score: What the Data Shows
Unfortunately, there isn't a publicly available, real-time database that tracks the exact number of people with a specific FICO score of 700. However, we can glean insights from aggregated credit score data and statistical analyses provided by credit bureaus and financial institutions.
While the specific percentage fluctuates over time due to various economic factors, studies consistently show that a significant portion of the population falls within the "Good" credit range (670-739). Therefore, a FICO score of 700 is relatively common, but it's not necessarily the average. The average FICO score in the United States typically hovers around the low 700s (e.g., 715-720), meaning a 700 score is slightly below the average. Think of it as being on the lower end of "Good," where you're doing well but can definitely aim higher.
Several factors influence the distribution of credit scores, including:
- Age: Older individuals generally have higher credit scores due to a longer credit history.
- Income: Higher income often correlates with better credit management.
- Geographic Location: Credit score averages can vary by state or region.
- Economic Conditions: Recessions and economic downturns can negatively impact credit scores.
Why "Good" is Good, But "Excellent" is Better
Having a 700 FICO score opens doors to many financial products and services, but striving for a higher score can unlock even more benefits. Here’s why aiming for an "Excellent" (740+) score is advantageous:
- Lower Interest Rates: With a higher score, you'll qualify for the lowest interest rates on loans and credit cards, saving you significant money over time. Even a slight decrease in interest can translate to thousands of dollars in savings on a mortgage.
- Better Credit Card Offers: Excellent credit scores unlock premium credit cards with attractive rewards programs, travel perks, and cashback opportunities.
- Increased Approval Odds: While a 700 score increases your chances of approval, an excellent score virtually guarantees it.
- Higher Credit Limits: Lenders are more willing to extend higher credit limits to individuals with excellent credit, providing greater financial flexibility.
- Improved Insurance Rates: In some states, insurance companies use credit scores to determine premiums. A higher score can lead to lower insurance costs.
Factors Influencing Your FICO Score
Understanding the factors that contribute to your FICO score is crucial for maintaining or improving it. The FICO scoring model considers five main categories:
- Payment History (35%): This is the most important factor. Paying your bills on time, every time, is crucial. Late payments, even by a few days, can negatively impact your score.
- Amounts Owed (30%): This refers to the amount of debt you owe compared to your credit limits (credit utilization). Keeping your credit utilization low (ideally below 30%) is essential. For example, if you have a credit card with a $1000 limit, try to keep your balance below $300.
- Length of Credit History (15%): The longer your credit history, the better. Lenders prefer to see a proven track record of responsible credit management.
- Credit Mix (10%): Having a mix of different types of credit (e.g., credit cards, installment loans) can positively impact your score. However, don't open accounts just to diversify your credit mix.
- New Credit (10%): Opening too many new credit accounts in a short period can lower your score. Lenders may see this as a sign of increased risk.
Deep Dive: Understanding Credit Utilization
Credit utilization, the ratio of your outstanding credit card balances to your total credit card limits, is a critical component of your FICO score. Keeping this ratio low demonstrates responsible credit management to lenders. Aim to keep your utilization below 30% on each individual card and across all your cards combined.
Example:
Let's say you have three credit cards with the following limits and balances:
- Card A: Limit $2000, Balance $400
- Card B: Limit $3000, Balance $900
- Card C: Limit $1000, Balance $200
To calculate your overall credit utilization:
- Total Credit Limit: $2000 + $3000 + $1000 = $6000
- Total Balance: $400 + $900 + $200 = $1500
- Credit Utilization: ($1500 / $6000) * 100 = 25%
In this scenario, your overall credit utilization is 25%, which is considered good. However, it's important to monitor the utilization on each individual card as well. Card B has a utilization of 30% ($900 / $3000), which is at the upper limit of what's considered ideal. Exceeding 30% on any one card can negatively affect your score.
Tips to Improve Your FICO Score (Even if it's Already 700)
Even if you have a 700 FICO score, there are always ways to improve it. Here are some actionable steps you can take:
- Pay All Bills On Time: This is the most important step. Set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you never miss a due date.
- Keep Credit Utilization Low: Aim for a credit utilization ratio below 30% on each card and overall. Consider paying down balances before the billing cycle ends to lower your reported utilization.
- Monitor Your Credit Report Regularly: Check your credit report from all three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) at least once a year for errors or inaccuracies. You can obtain a free copy of your credit report annually from AnnualCreditReport.com.
- Dispute Errors on Your Credit Report: If you find any errors on your credit report, dispute them with the credit bureau immediately.
- Avoid Opening Too Many New Accounts: Opening multiple new accounts in a short period can lower your score.
- Don't Close Old Credit Card Accounts: Closing old credit card accounts can reduce your overall available credit, potentially increasing your credit utilization ratio. If you have old accounts with no annual fees, consider keeping them open and using them occasionally to maintain activity.
- Consider a Secured Credit Card: If you have limited or no credit history, a secured credit card can be a good way to build credit.
- Become an Authorized User on Someone Else's Account: If a trusted friend or family member has a credit card with a long history of responsible payments, becoming an authorized user on their account can help you build credit.
Leveraging Technology to Track and Improve Your Credit Score
Numerous apps and websites can help you track your credit score, monitor your credit report, and receive personalized recommendations for improvement. Some popular options include:
- Credit Karma: Offers free credit scores and credit reports from TransUnion and Equifax.
- Credit Sesame: Provides free credit scores, credit reports, and credit monitoring.
- Experian: Offers access to your Experian credit report and credit monitoring services.
- MyFICO: Allows you to access your FICO scores from all three major credit bureaus.
These tools can help you stay informed about your credit health and identify areas where you can make improvements.
The Long-Term Benefits of a Strong Credit Score
Investing time and effort in building and maintaining a strong credit score pays off in the long run. A good credit score provides access to better financial opportunities and can save you significant money over your lifetime.
Beyond lower interest rates and better credit card offers, a strong credit score can also impact other aspects of your life, such as:
- Mortgage Approval: A good credit score is essential for obtaining a mortgage with favorable terms.
- Rental Applications: Landlords often check credit scores as part of the rental application process.
- Job Applications: Some employers may check credit scores as part of the hiring process, particularly for positions that involve financial responsibility.
- Utility Services: Utility companies may require a security deposit from individuals with poor credit.











